“Wisdom teeth dentistry explores solutions for pain and discomfort associated with emerging or impacted third molars. This article delves into understanding wisdom teeth, their potential impact on oral health, and recognizing signs of pain. We outline common treatment options, from surgical extraction with detailed procedures and post-op care to non-surgical approaches. Discover expert insights on managing wisdom tooth issues for a healthier smile.”
Understanding Wisdom Teeth and Their Impact on Oral Health
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last set of teeth to emerge, often appearing in late adolescence or early adulthood. While some people’s wisdom teeth grow in fully and remain healthy, many experience impaction or partial eruption, leading to discomfort and potential oral health issues. Impaction occurs when the tooth doesn’t have enough room to erupt properly, causing pain, inflammation, and even infection.
In cases of impaction or partial eruption, wisdom teeth dentistry offers various solutions. These include extractions to remove problematic wisdom teeth completely, or orthodontic treatments to realign the jaw and create space for their proper eruption. Regular dental check-ups are crucial in monitoring the health of wisdom teeth and addressing any issues early on to prevent complications that may require more extensive procedures.
Recognizing the Signs of Wisdom Tooth Pain
Wisdom tooth pain is a common issue that requires attention from dental professionals, especially in the field of wisdom teeth dentistry. Recognizing the signs early on can prevent further complications and discomfort. One of the initial indicators is severe pain or tenderness in the jaw, especially around the back molars, where wisdom teeth typically erupt. This pain might radiate to the side of the face, making it uncomfortable to chew or even open the mouth fully. Swelling gums, redness, and a bad taste in the mouth are also common symptoms associated with impending wisdom tooth issues. If you experience persistent pain, it’s advisable to consult a dentist specializing in wisdom teeth dentistry for an examination. They can identify if the wisdom teeth are impacted, partially erupted, or causing other dental problems, providing suitable solutions for effective pain management.
Common Treatment Options for Wisdom Teeth Issues

When dealing with wisdom teeth issues, several common treatment options are available in wisdom teeth dentistry. The primary goal is to alleviate pain and prevent potential complications like infection or damage to adjacent teeth. One option is extraction, which involves removing the tooth altogether. This is often recommended if the wisdom tooth is impacted, causing pain or posing a risk to nearby structures.
In some cases, dental professionals might opt for conservative management, such as oral antibiotics or over-the-counter pain relievers, to reduce inflammation and manage discomfort temporarily. Additionally, scaling and root planing can be performed to clean and smooth the tooth’s root surface, addressing any gum disease associated with impacted wisdom teeth. These treatments aim to buy time or alleviate symptoms before making a decision on more invasive procedures.
Surgical Extraction: Procedures and Post-Op Care
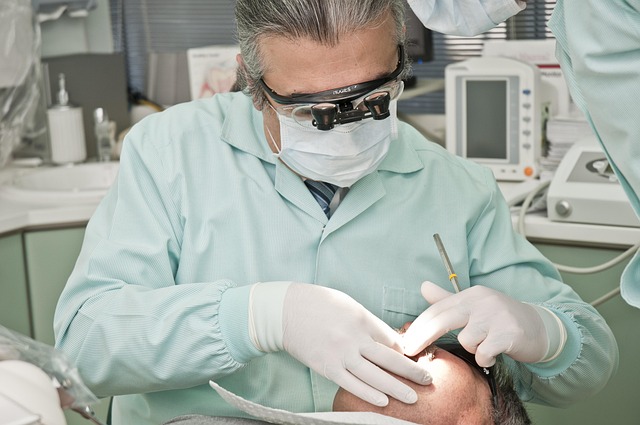
Surgical extraction is a common procedure for managing impacted or problematic wisdom teeth. This method involves a dental surgeon making a small incision in the gum to access and remove the tooth. The surgery is typically performed under local anesthesia, ensuring patient comfort. After the extraction, it’s crucial to follow the post-op care instructions provided by your dentist. This includes keeping the surgical site clean, using ice packs to reduce swelling, and restricting strenuous activities for a few days. It’s also important to take prescribed medications as directed and avoid certain foods that might irritate the extraction site. Proper aftercare is essential to prevent infection and promote healing.
The procedure itself varies depending on the complexity of the impaction. In some cases, the tooth may be partially erupted or angled incorrectly, making simple extraction challenging. Advanced techniques, such as sectioning the tooth into smaller pieces or using specialized instruments, might be required. Your dentist will discuss these options and recommend the best course of action to ensure a successful outcome in wisdom teeth dentistry.
Non-Surgical Approaches to Addressing Wisdom Tooth Discomfort

Many patients opt for non-surgical approaches when dealing with discomfort from erupting or impacted wisdom teeth. These methods focus on alleviating pain and promoting oral health without invasive procedures. One common technique is oral hygiene maintenance, which includes regular brushing and flossing around the wisdom teeth area to prevent infection and reduce inflammation. Additionally, over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can effectively manage discomfort and swelling.
Another non-surgical solution is the use of salt water rinses, such as warm salt water, which has anti-inflammatory properties and can help cleanse the gums around the wisdom teeth. In some cases, a dentist might recommend using a topical numbing agent to temporarily alleviate pain during the eruption process. These conservative methods aim to provide immediate relief while also addressing any underlying issues that contribute to the discomfort associated with wisdom teeth dentistry.
Wisdom teeth dentistry is a crucial aspect of maintaining optimal oral health, especially when dealing with pain and discomfort. By understanding the impact of wisdom teeth and recognizing the signs of impending issues, individuals can take proactive measures. The article has explored various treatment options, from surgical extraction with meticulous post-op care to non-surgical approaches, offering diverse solutions for a range of wisdom tooth problems. Whether considering wisdom teeth dentistry for pain relief or prevention, these strategies ensure a comprehensive approach to managing this common oral health challenge.
